メトキシケイヒ酸エチルヘキシルは、基本的に安全&内分泌撹乱作用に注意【安全性評価】

日焼け止めの成分メトキシケイヒ酸エチルヘキシルはUV-B(280nm~320nm)を吸収する性質があり、商品ではSPFに関係する成分です。UV-Bは肌の浅いところまで届く紫外線で、これを防いでくれますが、メトキシケイヒ酸エチルヘキシルは無毛マウスによる動物実験において内分泌かく乱作用、ホルモン撹乱作用があるため、過剰な利用にはリスクが伴います。
メトキシケイヒ酸エチルヘキシルとは
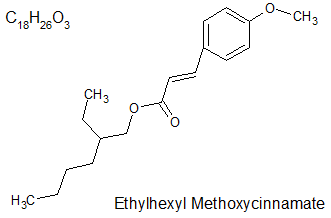
メトキシケイヒ酸エチルヘキシルは、オクチノキサートとも呼ばれ、IUPAC名:2-Ethylhexyl (2E)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate、化学式C18H26O3、モル質量290.403 g/mol、融点−25 ℃で、R体、S体、E体、Z体という4つの立体異性体を有する物質です。
極大吸収波長は308nm(PubChemでは310nm)なため、厳密にはUV-Bの全てを防げるわけではありませんが、オクトクリレンなどの他の紫外線吸収剤と一緒に使われるため、欠点は補われています。
経皮吸収やフリーラジカル発生があるため、特に目に入れてはいけません。コンタクトレンズを使っている方は、日焼け止めを使った手でそのままコンタクトレンズを目に入れたりすると刺激を受けて目がヒリヒリするかもしれません。目に間違って入った場合には流水でしっかり洗って様子を見て、異常があればすぐに医師に相談しましょう。
リスク1:肌から吸収される
表皮と呼ばれる肌の浅い所まで到達するUV-B(280nm~320nm)を吸収する能力がありますが、紫外線吸収に伴って化学的に変化し、肌に良くない影響を残すことがあります。フリーラジカル、一重項酸素と呼ばれる反応性の高い状態を保持する場合がありますが、医学的にその悪影響については人体での研究が及んでいません。
リスク2:エストロゲンに似たホルモン撹乱



上記の3種類のエストロゲンと呼ばれるホルモンに似ていると身体が判断してしまい、内分泌撹乱作用が出てしまう可能性があります。幼い子供、妊娠中の方、男性などホルモンの影響を受けやすい状態にある方は過剰な利用に注意が必要です。
肝臓障害があり、エストロゲンの分解が追いつかなくなった場合は、男性は乳腺肥大、女性は性周期が乱れる可能性があります。エストロゲンは女性の更年期にも分泌が増加するため、日焼け止めを多用する更年期の女性は少し注意すべきです。
リスク3:湿布と一緒に併用してはいけない
オクトクリレンと同様に、UV吸収能力と皮膚への吸収が起こる上に、日光照射で反応性の強いフリーラジカルを発生します。このため、日焼け止めと湿布を一緒に使用するとその部位が炎症を起こして赤くなる可能性があります。
メトキシケイヒ酸エチルヘキシル入りの日焼け止めを塗った場所に、直接湿布を貼らなくても、肌に吸収されるため、その周辺部位に湿布があれば肌荒れを起こす可能性があります。
毒性について
毒性に関する実験を見る限りでは、人体に対してこれといって有害だったとする臨床結果は見受けられませんでした。リスクに関しては可能性の域を出ないということをお忘れなく。
Agricultural workers are encouraged to use sunscreen to decrease the risk of UV-related skin cancer. … Previous studies have shown certain commercial sunscreens to be penetration enhancers. The focus of this project is to determine whether active ingredients in sunscreen formulations (i.e., the UV absorbing components and insect repellants for the sunscreen/bug repellant combinations) also act as dermal penetration enhancers for herbicides in vitro. The total percentages of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) penetrating through hairless mouse skin in 24 hr ranged from 54.9 +/- 4.7 for the no sunscreen control to 86.9 +/- 2.5 for padimate-O. Of the active ingredients tested (7.5% octyl methoxycinnamate, 7% octocrylene, 0.6% oxybenzone, 5% homosalate, 5% octyl salicylate, 8% padimate-o, 10% sulisobenzone, and 9.5% and 19% N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide (DEET)), all but octocrylene led to a significant increase in total 2,4-D penetration as compared to the control (P < 0.05), and only octocrylene and oxybenzone did not significantly decrease the corresponding lag time. Octyl salicylate (P < 0.01) and octyl methoxycinnimate (P < 0.05) significantly increased the 3H2O penetration across mouse skin, indicating physical damage to the stratum corneum. Additional studies demonstrated that the penetration enhancement seen across hairless mouse skin also occurred with human skin. Thus, the active ingredients of sunscreen formulations enhance dermal penetration of the moderately lipophilic herbicide 2,4-D.
(Pont AR et al; Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 195 (3): 348-54 (2004))
農業従事者は、紫外線に関連した皮膚がんのリスクを減らすために日焼け止め剤を使用することをお勧めします。/著者の/以前の研究は、ある種の市販の日焼け止め剤が浸透促進剤であることを示しています。このプロジェクトの焦点は、日焼け止め配合物中の活性成分(すなわち、日焼け止め/虫除け剤の組み合わせのための紫外線吸収成分および防虫剤)がインビトロで除草剤のための皮膚浸透促進剤としても作用するかどうかを決定することである。無毛マウスの皮膚を24時間で浸透する2,4- ジクロロフェノキシ酢酸(2,4-D)の総百分率は、無日焼け防止剤対照の54.9±4.7からパディメート−oの86.9±2.5の範囲であった。テストされた有効成分のうち(7.5%オクチルメトキシシンナメート、7%オクトクリレン、0.6%オキシベンゾン、5%ホモサレート、5%サリチル酸オクチル、8%パディメート-O、10%スルイソベンゾン、及び、9.5%と19%のN、N-ジエチル-m-トルアミド [ DEET ])が、すべてのオクトクリレンをするに至っ総2,4-Dの大幅な増加対照と比較して浸透(P <0.05)、そしてオクトクリレンおよびオキシベンゾンのみが対応する遅延時間を有意に減少させなかった。サリチル酸オクチル(P <0.01)およびオクチルメトキシシンニメート(P <0.05)はマウス皮膚を横切る(3)H 2 O浸透を有意に増加させ、角質層への物理的損傷を示した。さらなる研究は、無毛マウスの皮膚を横切って見られる浸透増強がまた人間の皮膚でも起こったことを示した。従って、日焼け止め配合物の活性成分は、適度に親油性の除草剤2,4-Dの皮膚浸透性を高める。
The authors/sought to determine whether the effect of preapplication of a sun protection factor (SPF) 29 sunscreen (containing octyl methoxycinnamate, oxybenzone, and octyl salicylate) could prevent local UVB-induced suppression of contact hypersensitivity to dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB). Nineteen subjects received either three minimal erythema doses of UVB daily on three consecutive days (UVB group) or sunscreen followed by this same dose of UVB irradiation (sunscreen plus UVB group) to a 16-sq cm area of the buttock. One day after completion of irradiation, DNCB was applied to this buttock site, and 2 weeks later, forearm challenge with four different concentrations of DNCB was performed. A control group of 10 subjects underwent DNCB testing as above, but with no prior exposure to UVB (no-UVB group). … The UVB group had a reduced response rate to all challenge doses of DNCB (3.125, 6.25, and 8.8 ug), except for the highest dose (12.5 ug) compared with the no-UVB control group (Fisher’s Exact test, P < or = 0.008), and compared with the sunscreen plus UVB group (P < or = 0.02). The no-UVB and sunscreen plus UVB groups showed no significant differences in response rates to any of the doses of DNCB tested (P > or = 0.53). … These results indicate that application of a sunscreen with over ninefold greater protection than that needed to prevent erythema prior to localized UVB radiation prevents localized UVB-induced suppression of contact hypersensitivity…
(Whitmore SE, Morison WL; Arch Dermatol 131 (10): 1128-33 (1995))
著者らは、日焼け防止剤(SPF)29日焼け止め剤(オクチルメトキシシンナメート、オキシベンゾン、およびオクチルサリチレートを含む)の前塗布の効果がジニトロクロロベンゼン(DNCB)に対する接触過敏症の局所UVB誘発抑制を防ぐことができるかどうかを調べた。19人の被験者が、3連続日に毎日3回の最小量の紅斑量のUVB(UVB群)または日焼け止めの後にこの同じ線量のUVB照射(日焼け止めとUVB群)のいずれかを臀部の16平方cm領域に受けた。照射完了の1日後に、DNCBをこの臀部部位に適用し、そして2週間後、4つの異なる濃度の前腕攻撃を行った。DNCBが実行されました。10人の被験者の対照群は、上記のようにDNCB試験を受けたが、UVBへの以前の曝露なしで(UVBなし群)。UVBグループは、DNCBのすべてのチャレンジ用量に対する奏効率が低下していました(3.125、6.25、及び、8.8μg)、ただし、非UVB対照群と比較した最高用量(12.5μg)、および日焼け止め剤+ UVB群との比較(P <=0.008、または、=0.02)。非UVB群および日焼け止め剤群+ UVB群は、試験したいずれの用量のDNCBに対しても奏効率に有意差を示さなかった(P>または=0.53)。これらの結果は、接触過敏症のUVB誘発抑制を局所化防止ローカライズUVB照射前に紅斑を防止するために必要よりも大きい保護を超えると日焼け止めの適用を示している。
The influence of sucrose laureate and sucrose oleate on the in vivo percutaneous penetration of octyl methoxycinnamate (OMC) formulated in i) colloidal suspensions (nano-emulsions and nanocapsules), and ii) conventional o/w emulsions was evaluated. The results showed that nano-emulsions formulated with sucrose laureate exhibited the highest penetration in the stratum corneum compared to the other formulations. A two-fold increase in OMC skin deposition was observed with the nano-emulsion containing sucrose laureate when compared to the control. The data obtained suggest that the total amount of OMC detected in the stratum corneum and the penetration depth are strongly dependent upon the formulation’s nature, the particle size, and the type of enhancer.
(Calderilla-Fajardo SB; Drug Dev Ind Pharm 32 (1): 107-13 (2006))
影響スクロースのインビボ経皮的侵入に受賞者とスクロースオレイン酸オクチルメトキシシンナメート Iで処方(OMC))コロイド懸濁液(ナノエマルジョンおよびナノカプセル)、及びii)は、従来のO / Wエマルションを評価しました。結果は、スクロースラウレートを配合したナノエマルジョンが他の配合物と比較して角質層中で最も高い浸透を示すことを示した。スクロースを含有するナノエマルジョンでは、OMC皮膚沈着の2倍の増加が観察された。対照と比較したときに賞賛する。得られたデータは、角質層中に検出されたOMCの総量および浸透深さが製剤の性質、粒径および増強剤の種類に強く依存することを示唆している。
Hairless mice were exposed to repeated doses of UV simulating the solar energy spectrum. After a rest period, 3 applications a week were made to an area of skin of 12-o-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate … Suitable controls were used. The test group was completely protected by 50 % a.i., and 7.5 % gave an effect equivalent to reducing the insolation four-fold. It had been suggested that the a.i. could itself have been a promoter, but there was no evidence of this.
European Commission; Reports of the Scientific Committee on Cosmetology (Ninth Series): 2-Ethylhexyl-4-methoxycinnamate (5466-77-3) p. 72 (1999). Available from, as of September 10, 2013
http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/scc_o_9.pdf
無毛マウスを太陽エネルギースペクトルをシミュレートした紫外線の反復線量にさらした。休息期間の後、週に3回、12-o-テトラデカノイルホルボール-13-アセテートの皮膚領域に塗布した。適切な対照を使用した。試験群は50%a.i.により完全に保護され、そして7.5%は日射量を4倍減少させるのと同等の効果を与えた。ai自体がプロモーターである可能性があると示唆されていましたが、これに関する証拠はありませんでした。
Diminish the penetration of ultraviolet (UV) light through the epidermis by absorbing UV radiation within a specific wavelength range. The amount and wavelength of UV radiation absorbed are affected by the molecular structure of the sunscreen agent. /Sunscreen agents, topical/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006.
特定の波長範囲内の紫外線を吸収することによって、表皮を通過する紫外線(UV)の透過を減らします。吸収される紫外線の量と波長は、日焼け止め剤の分子構造によって影響を受けます。
The objective of this study was to determine the influence of Transcutol CG concentration on the transdermal permeation and skin accumulation of two ultraviolet (UV) absorbers, 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzophenone (oxybenzone) and 2-octyl-4-methoxycinnamate (cinnamate). The concentration of the UV absorber was held constant at 6% (w/w) for all vehicle systems while the concentration of Transcutol CG was varied from 0 to 50% (w/w). Data showed that both UV absorbers exhibited increases in skin accumulation with increasing concentrations of Transcutol CG. Skin accumulation of oxybenzone was significantly (P<0.05) greater than that of cinnamate for all formulations investigated. Oxybenzone skin accumulation ranged from 22.9+/-2.8 ug/mg (0% Transcutol CG) to 80.8+/-27.2 ug/mg (50% Transcutol CG). Cinnamate skin accumulation ranged from 9.0+/-0.9 ug/mg to 39.8+/-12.2 ug/mg at 0 and 50% Transcutol CG, respectively. No significant differences were found in the transdermal permeation of oxybenzone or cinnamate for any of the formulations tested. The results of this study demonstrate that the inclusion of Transcutol CG in sunscreen formulations increases the skin accumulation of the UV absorbers oxybenzone and cinnamate without a concomitant increase in transdermal permeation.
(Godwin DA et al; Eur J Pharm Biopharm 53 (1): 23-7 (2002))
本研究の目的は、2つの紫外線(UV)吸収剤、2-ヒドロキシ-4-メトキシベンゾフェノン(オキシベンゾン)と2-オクチル-4-メトキシシンナメート(シンナメート)の経皮透過と皮膚蓄積に対するトランスクトール CG濃度の影響を決定することであった。UV吸収剤の濃度は、全てのビヒクル系について6%(w / w)で一定に保たれたが、一方、TranscutolCGの濃度は0から50%(w / w)まで変化した。データは、両方のUV吸収剤が、濃度が増加したトランスカトールCGと共に皮膚蓄積の増加を示すことを示した。オキシベンゾンの皮膚蓄積調査したすべての製剤について、シンナメートよりも有意に(P <0.05)大きかった。オキシベンゾン皮膚蓄積は、22.9±2.8μg / mg(トランスキュオールCG 0%)から80.8±27.2μg / mg(トランスキュオールCG 50%)の範囲であった。桂皮酸皮膚蓄積は、0および50%のトランスカットオールCGにおいて、それぞれ9.0±0.9μg / mgから39.8±12.2μg / mgの範囲であった。試験した製剤のいずれについてもオキシベンゾンまたはケイ皮酸塩の経皮透過に有意差は見られなかった。この研究の結果は、日焼け止め配合物中にトランスクトールCGを含めることが、経皮透過の増加を同時に伴わずにUV吸収剤オキシベンゾンおよびシンナメートの皮膚蓄積を増加させることを実証している。
ヒト毒性評価について(日本語訳)
/HUMAN EXPOSURE STUDIES/ In 10 subjects, patches were applied for 24 hours and the areas then exposed to a suberythematous dose of UV irradiation. There was no evidence of phototoxicity.
European Commission; Reports of the Scientific Committee on Cosmetology (Ninth Series): 2-Ethylhexyl-4-methoxycinnamate (5466-77-3) p. 71 (1999). Available from, as of September 10, 2013: http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/scc_o_9.pdf
/HUMAN EXPOSURE STUDIES/ A 10 % solution of a.i. in dimethylphthalate was used. A total of 58 subjects were recruited, 12 males and 46 females, aged 18-63. Of these, 6 subjects failed to complete the test for reasons unconnected with the experimental procedure. Induction applications were made on the skin of the back, for 24 hours with occlusion, 3 times a week for 9 applications. Following a rest period of 2 weeks, a further patch was now applied to a new site on the back for 24 hours with occlusion. The area was inspected at 0, 24 and 48 hours after removal of the patch. No adverse reaction was noted at any stage of the experiment.
European Commission; Reports of the Scientific Committee on Cosmetology (Ninth Series): 2-Ethylhexyl-4-methoxycinnamate (5466-77-3) p. 69 (1999). Available from, as of September 10, 2013: http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/scc_o_9.pdf
/HUMAN EXPOSURE STUDIES/ A Draize repeated insult patch test was carried out at a concentration of 2 % in 53 subjects. There was no sensitization. In 54 subjects, a formulation of 7.5 % a.i. in petrolatum was applied for 48 hours under occlusion for 11 applications. After a 14 day rest, a challenge application of a single dose was made. There was no adverse reaction. In an extensive series of patch tests carried out in man, the a.i. was found to be very rarely responsible for allergic contact effects.
European Commission; Reports of the Scientific Committee on Cosmetology (Ninth Series): 2-Ethylhexyl-4-methoxycinnamate (5466-77-3) p. 69 (1999). Available from, as of September 10, 2013: http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/scc_o_9.pdf
/HUMAN EXPOSURE STUDIES/ In 53 subjects, a Draize repeated insult patch test at a concentration of 2 % caused no irritation. In 54 subjects, a Draize repeated insult patch test of a 7.5 % dilution of a.i. in petrolatum caused no irritation.
European Commission; Reports of the Scientific Committee on Cosmetology (Ninth Series): 2-Ethylhexyl-4-methoxycinnamate (5466-77-3) p. 69 (1999). Available from, as of September 10, 2013: http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/scc_o_9.pdf
/HUMAN EXPOSURE STUDIES/ Occlusive applications of undiluted a.i. were made to 60 subjects, of whom 20 had sensitive skin. The applications were made for 24 hours. Observations at removal of the patches, and 24 and 48 hours later, showed no evidence of a reaction. In 51 male and female subjects, similar patch tests were carried out. The dilution of the a.i. (if any) was not stated. There was no irritation.
European Commission; Reports of the Scientific Committee on Cosmetology (Ninth Series): 2-Ethylhexyl-4-methoxycinnamate (5466-77-3) p. 69 (1999). Available from, as of September 10, 2013: http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/scc_o_9.pdf
/HUMAN EXPOSURE STUDIES/ Despite the enormous increase in sunscreen use, allergic contact (AC) and photoallergic (PA) reactions to ultraviolet (UV) filters are considered rare. To analyse the data from 2,715 patients who underwent photopatch testing at St John’s Institute of Dermatology during the period 1983-98. A retrospective analysis of all positive photopatch test episodes was undertaken with the results retrieved from the environmental dermatology database and further verified with the original archived patch test documentation for each individual patient. RESULTS: In 111 patients with positive reactions (4.1%), there were 155 AC or PA reactions to allergens in the photopatch test series. Eighty PA reactions were observed in 62 (2.3%) patients (32 men and 30 women, age range 28-75 years), with UV filters accounting for 52 positive reactions (65%), drugs 16 (20%), musk ambrette 11 (14%) and the antiseptic trichlorocarbanilide one (1%). The most common UV filter photoallergen was benzophenone-3 with 14 positive results, followed by benzophenone-10 (n = 9), isopropyl dibenzoylmethane (n = 6), p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) (n = 5), octyl dimethyl PABA (n = 5), butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane (n = 4), isoamyl methoxycinnamate (n = 2), ethyl methoxycinnamate (n = 2), octyl methoxycinnamate (n = 2), amyl dimethyl PABA (n = 2) and phenylbenzimidazole sulphonic acid (n = 1). A similar number of AC reactions to UV filters was detected in this study. Thus 49 patients (1.8%) had a total of 75 reactions: 51 due to UV filters and 24 as a result of exposure to fragrances and therapeutic agents. Benzophenone-10 accounted for 13 AC reactions and benzophenone-3 for eight reactions. Twenty-two patients had a PA reaction alone, whereas 19 patients had chronic actinic dermatitis and 15 patients polymorphic light eruption (PLE) in addition. Thus, 34 of the 62 patients (55%) had a preceding underlying photodermatosis. These results show a low yield of positive photopatch tests. Thus, despite the large increase in the use of UV filters over the last decade, the development of PA reactions remains rare. … PubMed Abstract
Darvay A et al; Br J Dermatol 145 (4): 597-601(2001)
/HUMAN EXPOSURE STUDIES/ … Eighty-two patients with clinical diagnosis of photoallergic contact dermatitis enter the study. These patients attended the Centro Dermatologico Federico Lleras Acosta (CDFLLA), the National Institute of Dermatology of Colombia between August 2001 and May 2003. Photopatch tests were performed using the standard series of sunscreens (Chemotechnique Diagnostics) and 6-methylcoumarin. Cetyl alcohol, phenoxyethanol, methylparabene, propylene glycol, triethanolamine, propylparabene, trichlorocarbanilide and dichromate were also included. The allergens were applied in duplicate on the healthy skin of the back and covered with opaque tape withdrawn 24 hr later, the panel on the right was irradiated with an ultraviolet A dose of 5 J/sq cm. The tests were read 24 hr after the application of the allergens, 24 and 72 hr post-irradiation. The readings were assessed according to the visual scoring system recommended by the International Contact Dermatitis Research Group. … Twenty-six patients (31.7%) showed positive photopatch test responses to one or several allergens. Four of them showed positive results to three components of the series and four patients to two components. Thirty-eight photoallergic and 18 allergic reactions were observed. Ultraviolet filters were the substances which more frequently produced positive photopatch test responses (30.5%). The most common ultraviolet filter photoallergen was benzophenone-3 with 22/82 positive results (26.8%), followed by octyl methoxycinnamate (8/82), benzophenone-4 and mexenone (2/82), phenylbenzimidazole sulphonic acid, methylbenziliden camphor and octyl dimethyl PABA (1/82). One patient showed a photoallergic response to 6-methylcoumarin. There was a concordance between the allergen which elicited the positive response and the use of different substances which contained that molecule among its compounds in 17 patients (65.3%). 19.5% of the patients (16/82) showed positive results to one or several allergens in the irradiated panel as well as in the unirradiated control site. These cases were diagnosed as contact allergy, probably caused by aeroallergens, presenting a natural history and a clinical picture similar to photocontact allergy. The most common allergen was dichromate with 10 positive results… The results of this study confirm that sunscreens are the more frequently involved substances in photoallergic contact dermatitis in our population. Identification of the photoallergen is the key element for adequate disease control and patient education. PubMed Abstract
Rodriguez E et al; Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 22 (4): 189-92 (2006)
/HUMAN EXPOSURE STUDIES/ …Out of … 61 patients /with suspected allergy to sunscreen/, 5 were found to have positive patch test reactions to sunscreens. 2 were photoallergic, and 3 were allergic to active ingredients in sunscreens. The main causative allergens were 2-ethylhexyl-4-methoxycinnamate (Parsol MCX) and 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzophenone (oxybenzone). /The authors conclude that sunscreen contact allergy is uncommon in /their/ practice. PubMed Abstract
Ang P et al; Am J Contact Dermat 9 (1): 42-4 (1998)
/HUMAN EXPOSURE STUDIES//The authors/ assessed the ability of two sunscreens, with different spectral profiles, to inhibit DNA photodamage in human epidermis in situ. One formulation contained the established ultraviolet B filter octyl methoxycinnamate, whereas the other contained terephthalylidene dicamphor sulfonic acid, a new ultraviolet A filter. Both formulations had sun protection factors of 4 when assessed with solar simulating radiation in volunteers of skin type I/II. /The authors/ tested the hypothesis that sun protection factors would indicate the level of protection against DNA photodamage. Thus, /they/ exposed sunscreen-treated sites to four times the minimal erythema dose of solar simulating radiation, whereas vehicle and control sites were exposed to one minimal erythema dose. /They/ used monoclonal antibodies against thymine dimers and 6-4 photoproducts and image analysis to quantify DNA damage in skin sections. A dose of four times the minimal erythema dose, with either sunscreen, resulted in comparable levels of thymine dimers and 6-4 photoproducts to one minimal erythema dose +/- vehicle, providing evidence that the DNA protection factor is comparable to the sun protection factor. The lack of difference between the sunscreens indicates similar action spectra for erythema and DNA photodamage and that erythema is a clinical surrogate for DNA photodamage that may lead to skin cancer. PubMed Abstract
Young AR et al; J Invest Dermatol 115 (1): 37-41 (2000)
/CASE REPORTS/ …Although rarely observed, we here describe the occurrence of a photoallergic contact dermatitis in a 55-year-old man after the use of two different sunscreens. Photopatch testing showed hypersensitivity reactions of the delayed type against three different chemical UV filters, 4-tert-butyl-4- methoxy-dibenzoylmethane (Parsol 1789), 2-ethylhexyl-p-methoxycinnamate (Parsol MCX), and isoamyl-p-methoxycinnamate (Neoheliopan). PubMed Abstract
Collaris EJ, Frank J; Int J Dermatol 47 Suppl 1: 35-7 (2008)
/CASE REPORTS/ In a 71-year-old male Caucasian patient with persistent eczema on light-exposed skin, photocontact allergy was demonstrated to the UV filter substances 4-methylbenzylidene camphor (UVB), octyl methoxycinnamate (UVB), benzophenone-3 (UVA) and butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane (UVA) present in sunscreen products used by the patient over several years. A significantly reduced UVB sensitivity of 25 mJ/sq cm in this patient (normal minimal erythema dose in our laboratory = 70-130 mJ/sq cm) was considered an early indication of a persistent light reaction. Topical anti-inflammatory treatment over 2 weeks together with consequent application of a sunscreen containing Mexoryl SX/titanium dioxide led to complete remission. … PubMed Abstract
Schmidt T et al; Dermatology 196 (3): 354-7 (1998)
/ENDOCRINE MODULATION/ In this work, the estrogenic effects of three classes of substances included in cosmetic formulations-parabens, ultraviolet (UV) screens, and musk fragrances-were studied. Their estrogenic activity was measured with the use of three reporter cell lines: HELN, HELN ERalpha, and HELN ERbeta. These three cell lines allowed for the measurement of estrogenic activity toward estrogen receptors alpha and beta (ERalpha and ERbeta), while taking nonspecific interactions into account. Eight of the 15 substances tested showed specific estrogenic activity with the following degree of potency on ERalpha butylparaben > propylparaben > homosalate = octyl-dimethyl-PABA = 4-methyl-benzylidenecamphor = octyl-methoxycinnamate > ethylparaben = galaxolide. Among these active substances, parabens activated ERalpha and ERbeta similarly, UV screens activated ERalpha moderately and had almost no effect on ERbeta, and fragrances did not activate ERbeta… PubMed Abstract
Gomez E et al; J Toxicol Environ Health A 68(4): 239-51 (2005)
/ENDOCRINE MODULATION/ … Six frequently used UVA and UVB screens /were examined/ for estrogenicity in vitro and in vivo. In MCF-7 breast cancer cells, the five UVB filters, that is, benzophenone-3 (Bp-3), homosalate (HMS), 4-methyl-benzylidene camphor (4-MBC), octyl-methoxycinnamate (OMC), and octyl-dimethyl-PABA (OD-PABA), increased cell proliferation with median effective concentrations (EC(50)) values between 1.56 and 3.73 uM, whereas the UVA filter butyl-methoxydibenzoylmethane (B-MDM) was inactive. Further evidence for estrogenic activity was the induction of estrogen-dependent pS2 protein in MCF-7 cells and the blockade of the proliferative effect of 4-MBC by the estrogen antagonist ICI 182,780. PubMed Abstract Full text: PMC1240241
Schlumpf M et al; Environ Health Perspect 109 (3): 239-44 (2001)
/ENDOCRINE MODULATION/ The fact that certain ultraviolet (UV) filters used in cosmetics display estrogenic activity prompted us to study potential actions on androgen receptors (AR) in the human breast carcinoma cell line MDA-kb2, which expresses functional endogenous AR and glucocorticoid receptors (GR) and is stably transfected with a luciferase reporter plasmid. … The cell line was used for screening of UV filters, benzophenone-3 (Bp-3), benzophenone-4, 3-benzylidene camphor, 4-methylbenzylidene camphor, butyl-methoxy-dibenzoylmethane, homosalate (HMS), octyl-dimethyl-PABA, and octyl-methoxycinnamate. Two of these, Bp-3 and HMS, antagonized DHT-induced AR activation below cytotoxic concentrations, with IC50 of 5.57 10-6 M (HMS) and 4.98 10-6 M (Bp-3). None of the eight UV filters displayed agonistic activity when tested alone, but high concentrations of Bp-3 induced an increase of luciferase activity in the presence of dexamethasone, which was not blocked by hydroxyflutamide or the estrogen antagonist, ICI 182,780. These data indicate that the UV filters Bp-3 and HMS possess antiandrogenic activity in vitro in addition to estrogenic activity. PubMed Abstract
Ma R et al; Toxicol Sci 74 (1): 43-50 (2003)
/ENDOCRINE MODULATION/ The in vitro and in vivo estrogenicity of 5 UV B-filters, benzophenone-3 (Bp-3), homosalate (HMS), 4-methyl-benzylidene camphor (4-MBC), octyl-methoxycinnamate (OMC) and octyl-dimethyl-PABA (OD-PABA) and 1 UVA-filter, butyl-methoxydibenzoylmethane (B-MDM) were studied. A general screening assay (E-screen) with a human breast cancer cell line, MCF-7 cells, was carried out. A positive test was based upon the binding of the test compound with the estrogen receptor leading to cell proliferation. As a positive control, 17 b -estradiol, was used and it was, as expected, positive in the assay. The 5 UV-B filters were found to be positive in the assay and caused cell proliferation. The UV-A filter gave a negative result. EC 50 values for 17 b -estradiol, Bp-3, 4-MBC, OMC, OD-PABA and HMS were found to be 1.22 pM, 3.73 uM, 3.02 uM, 2.37 uM, 2.63 uM and 1.56 uM, respectively. The results were supported by the expression of the estrogen-dependent pS 2 protein and by an inhibition of effects with the anti-estrogen ICI 182,780.The potency of the positive control is in the order of picomoles; the in vitro potency of the UV-filters tested lays in the range of uM, which means a difference of 1 million units. The in vitro potency of the UV-filters is thus importantly lower than the one observed for 17 b -estradiol. Probably a lot of industrial chemicals would show some in vitro estrogenic effects when this type of comparisons is taken seriously. It should be emphasized here that in vitro assays can only demonstrate whether UV-filters bind on the estrogen receptor or not, but they do not provide evidence whether the compounds have estrogenic activity or not. In vitro assays are therefore screening tests useful in setting priorities for further in vivo testing. …Claiming that 5 UV-filters have estrogenic properties based on an in vitro test is premature. The in vitro ranking for the UV-filters going from Bp3, 4-MBC, OMC, OD-PABA to HMS, did not correspond with the in vivo results. Indeed, in the latter test 4-MBC was most active, followed by OMC and Bp-3. The most active UV-filter in vitro displayed only a weak activity in vivo. In addition OD-PABA and HMS were found to be inactive. Only precise toxicokinetic data can link the in vitro and in vivo data, a conclusion that was also reached by the authors.
European Commission; Opinion on the Evaluation of Potentially Estrogenic Effects of UV-filters adopted by the SCCNFP during the 17th Plenary meeting of 12 June 2001; Available from, as of October 21, 2013: http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/opinions/sccnfp_opinions_97_04/sccp_out145_en.htm
/ALTERNATIVE and IN VITRO TESTS/ …To analyze biological effects of OMC, an in vitro approach was used implying ultraviolet (UV) exposure of two human cell lines, a primary skin fibroblast (GM00498) and a breast cancer (MCF-7) cell line. End points include cell viability assessment, assay of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) and oxidated DNA lesions using alkaline elution and lesion-specific enzymes, and gene expression analysis of a panel of 17 DNA damage-responsive genes. /Investigators/ observed that OMC provided protection against CPDs, and the degree of protection correlated with the OMC-mediated reduction in UV dose. No such protection was found with respect to oxidative DNA lesions. Upon UV exposure in the presence of OMC, the gene expression studies showed significant differential changes in some of the genes studied and the expression of p53 protein was also changed. For some genes, the change in expression seemed to be delayed in time by OMC. The experimental approach applied in this study, using a panel of 17 genes in an in vitro cellular system together with genotoxicity assays, may be useful in the initial screening of active ingredients in sunscreens. PubMed Abstract Full text: PMC2840218
Duale N et al; Toxicol Sci. 114 (2): 272-84 (2010)
/OTHER TOXICITY INFORMATION/ Risk assessment and margin of safety for OMC. According to European Union Scientific Committee on Cosmetic Products and Non-Food Products (SCCNFP) notes of guidance The safety of octyl methoxycinnamate (OMC) has been reviewed by the SCC(SPC/1037/93, S28) in 1993. It was concluded that the compound has a low acute toxicity. OMC is not irritating or sensitizing in animals, but can be very rarely responsible for allergic contact dermatitis in man. Mutagenicity, photomutagenicity and photoclastogenicity tests were negative. The teratogenic activity has a NOAEL of more than 500 mg/kg bw/day, which was the highest dose tested. The percutaneous absorption was estimated to be 2%, a figure derived from experiments in human and animal skin in vitro, plus the results of an in vivo human study via oral uptake. The MoS /margin of safety/ was calculated to be 750, which is acceptable. …The NOEL (estrogenic activity) of OMC in the uterotrophic assay in immature Long-Evans rats was 522 mg/kg bw/day…The " Screening MoS" = 870, which would be acceptable (>100).
European Commission; Opinion on the Evaluation of Potentially Estrogenic Effects of UV-filters adopted by the SCCNFP during the 17th Plenary meeting of 12 June 2001. Available from, as of November 15, 2003: http://ec.europa.eu/health/ph_risk/committees/sccp/docshtml/sccp_out145_en.htm
/OTHER TOXICITY INFORMATION/ Topical use of sunscreens reduces the risk for sunburn in humans. Sunscreens probably prevent squamous-cell carcinoma of the skin when used mainly during unintentional sun exposure. No conclusion can be drawn about the cancer-preventive activity of topical use of sunscreens against basal-cell carcinoma and cutaneous melanoma. Use of sunscreens can extend the duration of intentional sun exposure, such as sunbathing. Such an extension may increase the risk for cutaneous melanoma. /Sunscreens/
IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Cancer-Preventive Agents (2001) Sunscreens (IARC Handbooks of Cancer Prevention, Vol. 5), Lyon, IARC; Unit of Chemoprevention: Cancer-Preventive Effects of Sunscreens.
/OTHER TOXICITY INFORMATION/ The manufacturers of sunscreen preparations with propellants warn that concentrating and subsequently inhaling the fumes from these preparations may be harmful or fatal. /Propellants/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2013; Drug Information 2013. Bethesda, MD. 2013
/ヒトの曝露試験/ 10人の被験者において、パッチを24時間貼付した後、その領域を紅斑以下の量のUV照射にさらした。光毒性の証拠はありませんでした。
欧州委員会レポートの科学委員会での化粧品(第9 シリーズ):2-エチルヘキシル-4-メトキシ(5466-77-3)のp。71(1999)に記載されている。利用可能な、よりなどの年9月10 日:2013年
http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/scc_o_9.pdf
/人体ばく露試験/ フタル酸ジメチル中のaiの10%溶液を使用した。18〜63歳の合計58人の被験者、すなわち男性12人、女性46人を募集した。これらのうち、6人の被験者は実験手順と関係のない理由でテストを完了できませんでした。誘導適用は、閉塞を伴って24時間、9適用について週3回、背中の皮膚に行われた。2週間の休息期間の後、さらにパッチを裏側の新しい部位に24時間閉塞して適用しました。パッチの除去後0、24および48時間で領域を検査した。実験のどの段階でも有害反応は見られなかった。
/人体ばく露試験/ A 53人の被験者に2%の濃度でドレイズ反復侮辱パッチ試験を実施した。感作はありませんでした。54人の被験者において、11回の施用のために、ワセリン中7.5%aiの製剤を閉塞下で48時間施用した。14日の休息の後、単回投与のチャレンジ適用を行った。副作用はありませんでした。ヒトで行われた広範囲の一連のパッチテストにおいて、aiがアレルギー性接触効果の原因となることはめったにないことがわかった。
/人体ばく露試験/ 53人の被験者において、2%の濃度でのDraize反復侮辱パッチテストは刺激を引き起こさなかった。54人の被験者において、ペトロラタム中7.5%希釈したaiのDraize反復侮辱パッチテストは刺激を引き起こさなかった。
/ヒトの暴露試験/希釈されていないaiの排他的塗布は60人の被験者に対して行われ、そのうち20人は敏感肌を有していた。申請は24時間行われた。貼付剤の除去時、および24および48時間後の観察では、反応の証拠は見られなかった。51人の男性および女性被験者において、同様のパッチテストが行われた。aiの希釈(もしあれば)は述べられていない。刺激はありませんでした。
日焼け止めの使用が大幅に増加しているにもかかわらず、紫外線(UV)フィルターに対するアレルギー性接触(AC)および光アレルギー性(PA)反応はまれであると考えられています。1983 – 98年の間にセントジョンズ皮膚科学研究所でフォトパッチテストを受けた2,715人の患者からのデータを分析すること。すべての陽性フォトパッチテストエピソードの遡及的分析は、環境皮膚科データベースから検索された結果を用いて行われ、そして各個々の患者についてオリジナルのアーカイブパッチテスト文書を用いてさらに検証された。結果:陽性反応(4.1%)を有する111人の患者において、フォトパッチテストシリーズにおいてアレルゲンに対して155のACまたはPA反応がありました。62人(2.3%)の患者(男性32人、女性30人、年齢28〜75歳)で80のPA反応が観察された、トリクロロカルバニリド1(1%)。最も一般的なUVフィルターの光アレルゲンは14の肯定的な結果とベンゾフェノン-3、続いてベンゾフェノン-10(n = 9)、イソプロピルジベンゾイルメタン(n = 6)、p-アミノ安息香酸(PABA)(n = 5)、オクチルジメチルPABA(n = 5)、ブチルメトキシジベンゾイルメタン(n = 4)、イソアミルメトキシシンナメート(n = 2)、エチルメトキシシンナメート(n = 2)、オクチルメトキシシンナメート(n = 2)、アミルジメチルPABA(n = 2)およびフェニルベンズイミダゾールスルホン酸(n = 1)。この研究では、UVフィルターと同数のAC反応が検出されました。したがって、49人の患者(1.8%)が合計75の反応を持っていた:51はUVフィルターによるものであり、24は香料および治療薬への暴露の結果としてである。ベンゾフェノン−10が13個のAC反応を占め、ベンゾフェノン−3が8個の反応を占めた。22人の患者が単独でPA反応を示したのに対し、19人の患者は慢性日光性皮膚炎を患っており、15人の患者はさらに多形性光疹(PLE)を患っていた。したがって、62人の患者のうち34人(55%)に先行する基礎的光皮膚症があった。これらの結果はポジティブフォトパッチ試験の収率が低いことを示している。したがって、過去10年間でUVフィルターの使用が大幅に増加したにもかかわらず、PA反応の開発はまれです。
Darvay A 等 。 Br J Dermatol 145 (4): 597-601(2001)
光アレルギー性接触皮膚炎の臨床診断を受けた82人の患者がこの研究に加わる。これらの患者は、セントロ出席Dermatologico 2003 Photopatchテストは、標準的な日焼け止めのシリーズ(Chemotechnique診断)とを使用して実施した2001年8月と月の間フェデリコLlerasアコスタ(CDFLLA)、コロンビアの皮膚科の研究所を6メチルクマリンを。セチルアルコール、フェノキシエタノール、メチルパラベン、プロピレングリコール、トリエタノールアミン、プロピルパラベン、トリクロロカルバニリドおよび重クロム酸塩含まれていた。アレルゲンを背中の健康な皮膚に二重に塗布し、24時間後に引き出された不透明テープで覆い、右側のパネルに5J / cm2の紫外線A線量を照射した。試験は、アレルゲンの適用後24時間、照射後24および72時間に行った。測定値は、International Contact Dermatitis Research Groupによって推奨されているビジュアルスコアリングシステムに従って評価した。26人の患者(31.7%)が1つまたは複数のアレルゲンに対して陽性の光パッチテスト反応を示した。それらのうちの4つはシリーズの3つの構成要素と2つの構成要素に4人の患者に肯定的な結果を示しました。38のアレルギー反応と18のアレルギー反応が観察されました。紫外線フィルターは、ポジティブフォトパッチテスト応答(30.5%)をより頻繁に生じる物質でした。22/82の肯定的な結果(26.8%)のベンゾフェノン-3、続いてオクチルメトキシシンナメート(8/82)、ベンゾフェノン-4およびメキセノン(2/82)、フェニルベンズイミダゾールスルホン酸、メチルベンジリデンカンファーおよびオクチルジメチルPABA(1/82) 。1人の患者が6-メチルクマリンに対して光アレルギー反応を示しました。陽性反応を誘発したアレルゲンと17人の患者のその化合物の中でその分子を含む異なる物質の使用との間に一致があった(65.3%)。患者の19.5%(16/82)が、照射を受けたパネルおよび未照射の対照部位において1つまたは複数のアレルゲンに対して陽性の結果を示した。これらの症例は、おそらくアレルギー性アレルギーによって引き起こされる接触アレルギーと診断され、自然史および光接触アレルギーに類似した臨床像を提示している。最も一般的なアレルゲンは重クロム酸塩でしたこの研究の結果は、日焼け止め剤が我々の母集団における光アレルギー性接触皮膚炎においてより頻繁に関与する物質であることを確認しています。光アレルゲンの同定は、適切な疾病管理と患者教育のための重要な要素です。
Rodriguez E ら 。 Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 22 (4): 189から92 (2006)
61人の患者/日焼け止めアレルギーが疑われる/ 5人が日焼け止めに対する陽性パッチテスト反応を示した。2人は光アレルギー性であり、そして3人は日焼け止め剤中の活性成分に対してアレルギー性であった。主な原因となるアレルゲンは、2-エチルヘキシル-4-メトキシシンナメート(Parsol MCX)および2-ヒドロキシ-4-メトキシベンゾフェノン(オキシベンゾン)であった。/著者は、日焼け止め接触アレルギーは/彼らの/実践では珍しいと結論を下しました。
Ang P et al。 Am J Contact ダーマット 9 (1): 42-4 (1998)
著者らは、異なるスペクトルプロファイルを有する2つの日焼け止め剤がin situでヒト表皮のDNA光損傷を阻害する能力を評価した。一方の配合物は確立された紫外線Bフィルターオクチルメトキシシンナメートを含有し、他方はテレフタリリデンジカンファースルホン酸を含有した。、新しい紫外線Aフィルター。両タイプの配合物は、皮膚タイプI / IIの志願者において太陽光模擬放射線で評価した場合に4の日焼け防止係数を有した。/著者は/日焼け防止要因はDNAの光損傷に対する保護のレベルを示すだろうという仮説を検証しました。したがって、それらは、日焼け止め処理された部位を最小紅斑量の太陽光模擬放射線に4回暴露したが、ビヒクルおよび対照部位は1回の最小紅斑量に暴露された。彼らは、チミン二量体に対するモノクローナル抗体と6〜4の光生成物および画像解析を用いて皮膚切片のDNA損傷を定量化した。いずれかの日焼け止め剤を用いた場合の最小紅斑量の4倍の投与量は、同程度のレベルのチミンをもたらした。DNA保護因子が日焼け防止因子に匹敵するという証拠を提供して、1つの最小紅斑量+/-ビヒクルへの二量体および6-4光生成物。日焼け止め剤の間に違いがないことは、紅斑およびDNA光損傷について同様の作用スペクトルを示し、そして紅斑が皮膚癌を引き起こし得るDNA光損傷の臨床的代用物であることを示す。
Young AR et al; J Invest Dermatol 115 (1): 37-41 (2000)
/症例報告/ …めったに観察されないが、我々はここで2つの異なる日焼け止め剤を使用した後の55歳の男性における光アレルギー性接触性皮膚炎の発生について説明する。フォトパッチテストは、3つの異なる化学UVフィルター、4-tert-ブチル-4-メトキシ-ジベンゾイルメタン(Parsol 1789)、2-エチルヘキシル-p-メトキシシンナメート(Parsol MCX)、およびイソアミル-p-メトキシシンナメートに対する遅延型の過敏反応を示した。(ネオヘリオパン)。
Collaris EJ、 Frank J; Int J Dermatol 47 Suppl 1: 35-7 (2008)
CASEは、光露出した皮膚の永続湿疹を有する71歳の白人男性患者において、photocontactアレルギーは、UVフィルター物質に実証された/レポート4-メチルベンジリデンカンファー、(UVB)メトキシ桂皮酸オクチル(UVB)、ベンゾフェノン-3(数年間にわたって患者によって使用されている日焼け止め製品中に存在するUVA)およびブチルメトキシジベンゾイルメタン(UVA)。この患者における25mJ / cm2の有意に低下したUVB感度(我々の研究室における通常の最小紅斑線量= 70~130mJ / cm2)は、持続性光反応の初期の兆候と考えられた。一緒に含有する日焼け止め剤の結果として適用した2週間にわたる局所的な抗炎症治療MEXORYL SXを /二酸化チタンは完全な寛解につながりました。
Schmidt T et al。 Dermatology 196 (3): 354-7 (1998)
この研究では、化粧品に含まれる3種類の物質(パラベン、紫外線(UV)スクリーン、およびムスク香料)のエストロゲン様作用を調べました。それらのエストロゲン活性は、3つのレポーター細胞株:HELN,HELN ERアルファ、およびHELN ERベータを使用して測定された。これら3つの細胞株は、非特異的相互作用を考慮に入れながら、エストロゲン受容体αおよびβ(ERαおよびERβ)に対するエストロゲン活性の測定を可能にした。試験した15の物質のうち8つは、以下の程度の効力を有するERα ブチルパラベン > プロピルパラベン > ホモサレート =オクチル – ジメチル-PABA=4-メチル-ベンジリデンカンファー=オクチル-メトキシシンナメートで特定のエストロゲン様活性を示した。エチルパラベン=ガラキソリド。これらの活性物質の中で、パラベンは同様に、UVスクリーンは適度ERアルファを活性化し、ERbetaにほとんど影響を与えなかった、と香りがERbetaを活性化しなかったERアルファとERbeta活性化。
Gomez E et al。 J Toxicol Environ Health A 68(4): 239-51 (2005)
6つの頻繁に使用されるUVAおよびUVBスクリーンは、in vitroおよびin vivoでエストロゲン性について検査されました。MCF-7乳がん細胞では、5つのUVBフィルター、すなわち、ベンゾフェノン-3(Bp-3)、ホモサレート(HMS)、4-メチル-ベンジリデンカンファー(4-MBC)、オクチル-メトキシシンナメート(OMC)、およびオクチル-ジメチル-PABA(OD – PABA)は1.56から3.73μMの間の中央有効濃度(EC50)値で細胞増殖を増加させたが、一方UVAフィルターのブチル-メトキシジベンゾイルメタン(B-MDM)は不活性であった。エストロゲン活性のさらなる証拠は、MCF-7細胞におけるエストロゲン依存性pS2タンパク質の誘導および4-MBCの増殖効果の遮断であったエストロゲン拮抗薬によるICI 182,780。
Schlumpf M et al。 Environ Health Perspect 109 (3): 239-44 (2001)
/内分泌調節/化粧品に使用される特定の紫外線(UV)フィルターがエストロゲン様活性を示すという事実は、機能的な内因性ARおよびグルココルチコイド受容体を発現するヒト乳癌細胞株MDA-kb2のアンドロゲン受容体(AR)に対する潜在的作用の研究を促しました(GR)であり、ルシフェラーゼレポータープラスミドで安定にトランスフェクトされている。…細胞株はUVフィルターのスクリーニングのために使用したベンゾフェノン-3(BP-3)、ベンゾフェノン-4、3-ベンジリデンカンファー、4-メチルベンジリデンカンファー、ブチルメトキシジベンゾイルメタン、ホモサレート(HMS)、オクチルジメチルPABA、オクチルメトキシケイ皮酸。これらのうちの2つ、Bp-3およびHMSは、細胞傷害性濃度未満でDHT誘導性AR活性化に拮抗し、IC 50は5.57×10 -6M(HMS)および4.98×10 -6M(Bp-3)であった。単独で試験した場合、8つのUVフィルターのどれもアゴニスト活性を示さなかったが、高濃度のBp-3はデキサメタゾンの存在下でルシフェラーゼ活性の増加を誘導し、それはヒドロキシフルタミドまたはエストロゲンアンタゴニスト、ICI 182,780によって遮断されなかった。これらのデータは、UVフィルターBp -3およびHMSがエストロゲン活性に加えてインビトロで抗アンドロゲン活性を有することを示している。
Ma R et al。 Toxicol Sci 74 (1): 43-50 (2003)
/内分泌調節/ 5種類のUV Bフィルター、ベンゾフェノン-3(Bp-3)、ホモサレート(HMS)、4-メチル – ベンジリデンカンファー(4-MBC)、オクチル – メトキシシンナメート(OMC)のin vitroおよびin vivoエストロゲン作用オクチル – ジメチル−PABA(OD – PABA)および1UVA-フィルタ、ブチル – メトキシジベンゾイルメタン(B – MDM)を研究した。ヒト乳癌細胞株、MCF-7細胞を用いた一般的なスクリーニングアッセイ(E-スクリーン)を実施した。陽性試験は、細胞増殖をもたらす試験化合物とエストロゲン受容体との結合に基づいた。陽性対照として、17 b – エストラジオール、を使用し、そしてそれは、予想通り、アッセイにおいて陽性であった。5つのUV-Bフィルターはアッセイにおいて陽性でありそして細胞増殖を引き起こしたことが見出された。UV-Aフィルターは否定的な結果を与えた。17b-エストラジオール、Bp-3、4-MBC、OMC、OD-PABAおよびHMSに対するEC 50値は、それぞれ1.22pM、3.73μM、3.02μM,2.37μM,2.63μMおよび1.56μMであることが分かった。結果は、エストロゲン依存性pS にタンパク質の発現および抗エストロゲンICI 182,780による効果の阻害によって支持された。陽性対照の効力はピコモル程度である。試験したUVフィルターのインビトロ効力はμMの範囲にあり、これは100万単位の差を意味する。したがって、UVフィルターのin vitroでの効力は、17b-エストラジオールで観察されたものよりも重要に低いです。この種の比較を真剣に考えると、おそらく多くの工業用化学物質がいくつかのin vitroエストロゲン効果を示すでしょう。ここで強調しておかなければならないのは、in vitroアッセイはUVフィルターがエストロゲン受容体に結合するか否かを示すことができるだけであるが、化合物がエストロゲン活性を有するか否かの証拠を提供しない。したがって、インビトロアッセイは、さらなるインビボ試験の優先順位を決めるのに有用なスクリーニング試験である。in vitro試験に基づいて5つのUVフィルターがエストロゲン様特性を持つと主張するのは時期尚早です。Bp3、4-MBC、OMC、OD-PABAからHMSまでに及ぶUVフィルターのインビトロランキングは、インビボの結果と一致しなかった。実際、後者のテストでは4 MBC最も活発であり、OMCとBp-3がそれに続いた。インビトロで最も活性のあるUVフィルターはインビボで弱い活性しか示さなかった。さらに、OD-PABAおよびHMSは不活性であることが見出された。正確な毒物動態学的データのみがin vitroおよびin vivoデータを結び付けることができ、これもまた著者によって達成された結論である。
欧州委員会意見の評価の潜在的エストロゲン効果のUV-フィルター採用によりSCCNFP の間に第17回総会の会議の12 年6月2001; 利用可能な、よりなどの年10月21 日:2013年http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/opinions/sccnfp_opinions_97_04/sccp_out145_en.htm
OMCの生物学的影響を分析するために、2つのヒト細胞系、原発性皮膚線維芽細胞(GM00498)および乳がん(MCF-7)の紫外線(UV)曝露を意味するin vitroアプローチを使用した。 )細胞株。評価項目には、細胞生存率評価、アルカリ溶出および損傷特異的酵素を用いたシクロブタン ピリミジンダイマー(CPD)および酸化DNA損傷の分析、ならびに17のDNA損傷応答遺伝子パネルの遺伝子発現分析が含まれます。/捜査官/ OMCがCPDに対する保護を提供したことを観察したそして、保護の程度は、UV線量のOMC媒介減少と相関していた。酸化的DNA損傷に関してそのような保護は見いだされなかった。OMCの存在下でUV照射すると、遺伝子発現試験は、試験した遺伝子のいくつかにおいて有意差のある変化を示し、そしてp53タンパク質の発現もまた変化した。いくつかの遺伝子については、発現の変化は、OMCによって時間的に遅れるように思われた。遺伝毒性アッセイと一緒にin vitro細胞系で17遺伝子のパネルを使用して、この研究に適用された実験的アプローチは、日焼け止め剤中の活性成分の最初のスクリーニングに有用であり得る。
Duale N et al。 トキシコル サイエンス 114 (2): 272-84 (2010)
OMCのリスク評価と安全性の限界。化粧品および非食品製品に関する欧州連合科学委員会(SCCNFP)のガイダンスノートによれば、オクチルメトキシシンナメートの安全性(OMC)は1993年にSCC(SPC / 1037/93、S28)によってレビューされている。化合物は急性毒性が低いと結論付けられた。OMCは動物に刺激や感作性はありませんが、人間のアレルギー性接触皮膚炎の原因となることはめったにありません。変異原性、光変異原性および光原性試験は陰性であった。催奇形性活性は、500 mg / kg bw /日を超えるNOAELを有し、これは試験された最高用量であった。経皮吸収は2%と推定され、これはインビトロでのヒトおよび動物の皮膚での実験、および経口摂取によるインビボでのヒト試験の結果に由来する数値である。MoS /安全域/は750であると計算され、これは許容可能である。未熟なLong-Evansラットの子宮栄養アッセイにおけるOMCのNOEL(エストロゲン様活性)は522 mg / kg体重/日でした。
欧州 委員会 意見 の評価の潜在的エストロゲン効果のUV-フィルター採用によりSCCNFP の間に第17回総会の会議の12 年6月2001年利用可能な、よりなどの年11月15 :2003 http://ec.europa.eu/health/ph_risk/委員会/ sccp / docshtml / sccp_out145_en.htm
日焼け止め剤の局所使用は、人の日焼けの危険性を減らします。日焼け止めは、主に意図的でない日光曝露の間に使用されるとき、おそらく皮膚の扁平上皮癌を予防します。基底細胞癌および皮膚黒色腫に対する日焼け止めの局所使用の癌予防活性について結論を引き出すことはできない。日焼け止め剤の使用は、日光浴などの意図的な日光暴露の期間を延ばすことができます。このような延長は、皮膚黒色腫のリスクを高める可能性があります。
IARCワーキンググループでの検討のがん予防エージェント(2001)日焼け止め(IARC ハンドブックのがん予防、巻5)、リヨン、IARC。単位の化学予防:がん予防効果の日焼け止め。
噴射剤を含む日焼け止め製剤の製造業者は、これらの製剤からのフュームの濃縮およびその後の吸入は有害または致命的である可能性があると警告しています。
アメリカの 社会 の 健康システム 薬剤師 2013; Drug Information 2013. ベセスダ、 メリーランド州。 2013年
参照リンク
PubChem
参照元:https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Octinoxate
資生堂 美容成分辞典
参照元:https://www.shiseidogroup.jp/ingredients/beauty-ingredients/ethylhexyl_methoxycinnamate.html
The dark side of chemical sunscreens. Should you be concerned about photosensitization?
参照元:http://www.smartskincare.com/skinprotection/chemical-sunscreen-risks.html
公益社団法人 日本皮膚科学会
参照元:https://www.dermatol.or.jp/qa/qa2/q03.html
Chemical UVB sunscreen/sunblock: octyl methoxycinnamate (octinoxate)
参照元:http://www.smartskincare.com/skinprotection/sunblocks/sunblock_octinoxate.html
エストロゲン Wikipedia
参照元:https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E3%82%A8%E3%82%B9%E3%83%88%E3%83%AD%E3%82%B2%E3%83%B3
Octyl Methoxycinnamate Modulates Gene Expression and Prevents Cyclobutane Pyrimidine Dimer Formation but not Oxidative DNA Damage in UV-Exposed Human Cell Lines
Posted by Medic
関連記事
ビスエチルヘキシルオキシフェノールメトキシフェニルトリアジンはほぼ問題なし|日焼け止めの成分チェック
ビスエチルヘキシルオキシフェノールメトキシフェニルトリアジンは、化粧品の成分とし ...

酸化チタンは吸入しなければ大丈夫|日焼け止めの成分チェック
酸化チタン(titanium oxide、主に酸化チタンⅣ:titanium(I ...

【安全性評価】キュレル湿潤保湿「化粧水Ⅲとてもしっとり」はニキビ対策に【乾燥性敏感肌向け】
ドラッグストアで約1500円で売っていたキュレル湿潤保湿化粧水の安全性評価と使用 ...
シクロペンタシロキサンとは – 吸入NG【安全性・毒性評価】
シクロペンタシロキサン(Cyclopentasiloxane)は、分子式はC10 ...

トリイソステアリン酸ポリグリセリル-2は基本無害|日焼け止めの成分チェック
トリイソステアリン酸ポリグリセリル-2(Polyglyceryl-2 Triis ...